The aim of this tutorial is to show the possibilities of the Fortinet SD-WAN solution in a real GUI interface on real use-cases. In this Tutorial will be configured Fortinet FortiGate SD-WAN solution with multiple WAN links and different configuration features for diverse real life use-cases.
SD-WAN is an automated, programmable wide-area network that dynamically and securely routes traffic based on applications policies, network conditions, or WAN link priority.
1. Intro
Advantages of SD-WAN:
- WAN Optimization – Increased bandwidth at lower cost
- Better bandwidth utilization thanks to better traffic direction control options between different WAN links as well as better control options for loadbalancing
- Increased application performance
- Centralized management across branch networks
- automated provisioning
- Full network visibility
- Providing organizations with more connection type options and vendor selection when building a network
- Improved edge-to-edge security
Fortinet SD-WAN designs principles:
The Five-pillar approach, described in the SD-WAN / SD-Branch Architecture for MSSPs guide, is recommended when designing a secure SD-WAN solution.
- Underlay – Choose the WAN links to use
- Overlay – Choose the topology to interconnect your sites
- Routing – Choose how to propagate routes between your sites
- Security – Choose how to protect each of the available paths
- SD-WAN – Choose the strategy used to pick one of the available paths
SD-WAN
The SD-WAN pillar is the intelligence that is applied to traffic steering decisions. It is comprised of four primary elements:
- SD-WAN zones
- SD-WAN is divided into zones. SD-WAN member interfaces are assigned to zones, and zones are used in policies as source and destination interfaces. You can define multiple zones to group SD-WAN interfaces together, allowing logical groupings for overlay and underlay interfaces. Routing can be configured per zone.
- See SD-WAN Zones
- SD-WAN members
- Also called interfaces, SD-WAN members are the ports and interfaces that are used to run traffic. At least one interface must be configured for SD-WAN to function.
- See Configuring the SD-WAN interface
- Performance SLAs
- Also called health-checks, performance SLAs are used to monitor member interface link quality, and to detect link failures. When the SLA falls below a configured threshold, the route can be removed, and traffic can be steered to different links in the SD-WAN rule.
- SLA health-checks use active or passive probing:
- Active probing requires manually defining the server to be probed, and generates consistent probing traffic.
- Passive probing uses active sessions that are passing through firewall policies used by the related SD-WAN interfaces to derive health measurements. It reduces the amount of configuration, and eliminates probing traffic. See Passive WAN health measurement for details.
- See Performance SLA
- SD-WAN rules
- Also called services, SD-WAN rules control path selection. Specific traffic can be dynamically sent to the best link, or use a specific route
- Rules control the strategy that the FortiGate uses when selecting the outbound traffic interface, the SLAs that are monitored when selecting the outgoing interface, and the criteria for selecting the traffic that adheres to the rule. When no SD-WAN rules match the traffic, the implicit rule applies.
- See SD-WAN rules
2. Prerequisites
- VMware ESXi host
- Fortinet FortiGate for VMWare ESXi platform Version 7.2.0
- three WAN link connections
3. Lab setup
In this use-case we have three Internet ISP links WAN1, WAN2, WAN3. Those links could have different characteristics e.g.:
Network Type
Connection Type
Guaranteed Speed
WAN1
Internet
Ethernet Cable
100 Mbps / 100 Mbps
WAN2
Internet
DSL
50 Mbps / 10 Mbps
WAN3
Internet
4G LTE
100 Mbps / 100 Mbps
To emulate diverse real world characteristics of the WAN links in my Testlab I have configured artificial parameters to this links as follows:
Latency
Jitter
Packet loss
WAN1
0
0
0
WAN2
+5 ms
0
0
WAN3
+10 ms
+8 ms
3%
4. Interfaces configuration
Every link will have a different cost configured which represents my personal link quality parameter. WAN3 link has the lowest cost number 10, because it has the lowest quality. WAN2 has cost 20 and WAN1 will have highest cost number 30, because it represents my primary WAN link which has the highest quality.
Example WAN2 Interface Configuration:
Configuration of all interfaces:
In this moment we have FortiGate lab appliance prepared for the SD-WAN configuration.
5. SD-WAN configuration elements
SD-WAN configuration typically consists of the following elements:
- SD-WAN interface members
- Performance SLAs
- SD-WAN rules
When using FortiManager to configure SD-WAN solution, all the above elements are conveniently packed into an SD-WAN template that can be applied to (a group of) your sites. However individual SD-WAN template could also be applied to each edge device, it is highly recommended (Fortinet best practice) grouping similar sites, and applying a single SD-WAN template to the entire group. This will significantly simplify the operations, and make the SD-WAN solution consistent.
Example SD-WAN Template Scheme:
6. SD-WAN zone configuration
Now I will create SD-WAN zone “virtual-wan-link” and will put “WAN1”, “WAN2”, “WAN3” Interfaces (SD-WAN members) into this SD-WAN zone. My primary link in this example is WAN1 therefore the priority is 1, WAN2 link will become priority 2, WAN3 will have priority 3.
In the next step default route will be configured and pointing to “virtual-wan-link”.
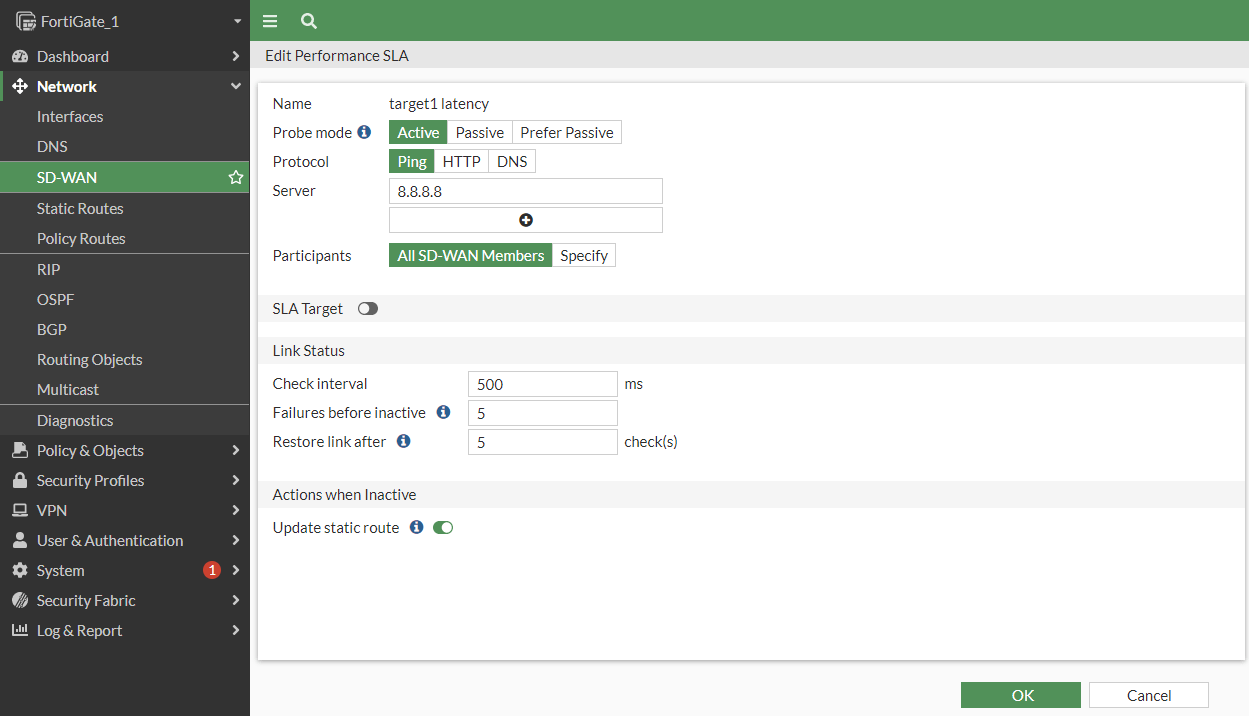
7. Performance SLA probe configuration
create Performance SLA probe for monitoring WAN1, WAN2, WAN3 links. In this use-case will be used simple Active Probe Mode without latency SLA Target against google 8.8.8.8 server for demonstration purposes.
Note: once the SD-WAN Performance SLA Probe is created, it starts to measure the SLA and it will be used in the SD-WAN member selection algorithm.
it is worth mentioning that in the production environment is very important to choose and decide for the best suited probe configuration. This depends on many individual factors such as:
- link parameters/type of connection e.g.:
- fibre optics – constant latency times, constant jitter, zero packet loss, high bandwidth – possible to configure more precise and sharper SLAs
- LTE – variable latency times, variable jitter, none to low packet loss (e.g. signal depending) – SLA Probe threshold ranges should be higher
- target selection
- first hop GW on the WAN link
- target IP in provider backbone
- target IP in peering DC
The Performance SLA Probe configuration differs from case to case and should be always tailored for the current use-case.
8. Performance SLA probe quick test
Now I will block WAN1 internet connection on the outgoing Firewall as a emulation of the outage in ISP backbone in real world (WAN1 GW is available, but behind WAN1 GW is the traffic blocked). Quick test of WAN1 outage shows that SD-WAN algorithm disables WAN1 link in the SD-WAN zone “virtual-wan-link” and will utilize the other links WAN2, WAN3 without any noticeable network outage on the user side. Monitoring events has been generated.
9. SD-WAN rules configuration
SD-WAN rules, which are sometimes called service rules, identify traffic of interest, and then route the traffic based on a strategy and the condition of the route or link between two devices. There are many possible strategies to select the outgoing interface and many performance service level agreements (SLAs) to evaluate the link conditions. (more about SD-WAN Rules)
SD-WAN rules strategies:
- Implicit rule
- Automatic strategy
- Manual strategy
- Best quality strategy
- Lowest cost (SLA) strategy
- Maximize bandwidth (SLA) strategy
- Use MAC addresses in SD-WAN rules and policy routes
- SD-WAN traffic shaping and QoS
- SDN dynamic connector addresses in SD-WAN rules
- Application steering using SD-WAN rules
- DSCP tag-based traffic steering in SD-WAN
- ECMP support for the longest match in SD-WAN rule matching
- Override quality comparisons in SD-WAN longest match rule matching
- Use an application category as an SD-WAN rule destination
For the purpose of demonstration I will be modeling SD-WAN rules for small branch with local break-out. This branch will be using following example set of applications:
Application
SIP Telephony
Microsoft Collaboration
File Sharing Services (onedrive)
Sharepoint
Backup Services
Properties/Requirements
realitime, low latency, low jitter
higher bandwidth, average latency
normal traffic
normal traffic
best effort
WAN link selection
WAN1, WAN2 – best quality (latency)
WAN1, WAN2 – best quality (bandwidth)
WAN3, WAN2 – maximize bandwidth (SLA)
WAN2, WAN1 – lowest cost (SLA)
WAN3, WAN2, WAN1 – lowest cost (SLA)
Strategies how outgoing interfaces will be chosen:
- Best Quality – The interface with the best measured performance is selected
- Lowest Cost (SLA) – The interface that meets SLA targets is selected. When there is a tie, the interface with the lowest assigned cost is selected
- Maximize Bandwidth (SLA) – Traffic is load balanced among interfaces that meet SLA targets
SD-WAN Rules configuration:
It is also visible (check mark) which members/WAN interfaces are used by each SD-WAN rule:
- SIP – primary WAN1 because of lower latency, WAN2 second
- Collaboration – best quality (quality criteria: bandwidth), WAN1 primary, WAN2 secondary
- Filesharing – loadbalancing between WAN2 and WAN3
- Sharepoint – lowest cost interface number when SLA is met, primary WAN2, secondary WAN1
- Backup – lowest cost interface number when SLA is met, primary WAN3, secondary WAN2, tertiary WAN1
10. SD-WAN rules test
10.1 WAN1 high latency
WAN1 link emulation parameters: latency +100ms, jitter +100ms
10.2 WAN2 high packet loss
WAN2 link emulation parameters: packet loss 20%
11. Knowledge
- what performance SLA probes destinations to chose?
- Depends on traffic patterns for the traffic, it is difficult to provide a general recommendation.
- For public cloud traffic, it is generally recommended to probe the respective cloud provider
- For general internet browsing, probing a public DNS could be a good option
- For corporate (site-to-site) traffic, it is recommended configuring a loopback interface on the hub, which the spokes will probe over all available overlays. This will allow them to compare the quality of different available transports without maintaining a dedicated health-check server behind the hub
- if you are creating performance SLA probe and you will use SD-WAN rules with Latency as a criteria, create the SLA probe with SLA Target. This will guarantee if the SLA will not be met, this SD-WAN member interface will not be used in the rule.
- e.g. our MS_Collaboration rule has Best Quality – Bandwidth strategy for outgoing interface chosen and is using Default_Office_365 SLA probe. This probe does not have Target SLA configured. That means the both interfaces WAN1, WAN2 are in use and traffic is loadbalanced unless the connectivity to o365 target is interrupted. If the SLA Target would be configured for latency/jitter/packet loss, the SD-WAN member interface will be not used if one of the SLA Targets is not met. e.g. latency over 200 ms or packet loss over 30% etc.
- Traffic flows
- corporate traffic (site-to-site) tt can be spoke-to-spoke, spoke-to-hub (when there are workloads behind the hub), or—rarely—hub-to-spoke.
- Direct internet access (DIA) is also known as local breakout, and this traffic leaves organization boundaries directly from the site edge.
- Remote internet access (RIA) is also known as remote breakout, and it means that the traffic must be backhauled through the hub (located in a datacenter or on MSSP premises).
- Cloud on-ramp provides optimized access to the workloads running in the cloud. Rather than accessing the cloud services through the public internet, an overlay can be established to the closest cloud POP in the area.
more about Traffic flows
12. Conclusion
SD-WAN provides WAN simplification, lower costs, bandwidth efficiency and a seamless on-ramp to the cloud with significant application performance especially for critical applications without sacrificing security and data privacy. Better application performance improves business productivity, customer satisfaction, and ultimately profitability. Consistent security reduces business risk.
Fortinet solution is according to the Gartner Magic Quadrant 2021 dominant leader n.1, which is well earned by the feature set, implementation, very good documentation materials and all diverse configuration combinations which offers this solution.
In this how to/tutorial I explained, how to configure SD-WAN Solution from Fortinet. All three basic SD-WAN configuration cornerstones: 1. SD-WAN interface members, 2. Performance SLAs, 3. SD-WAN rules. SD-WAN rules are serving only as an example and for demonstration purposes as well as idea for creating your own tailored SD-WAN rules. I have also picked out the most basic theory needed to understand SD-WAN solution. I hope this tutorial will help to understand and jump-start your new Fortinet SD-WAN journey.